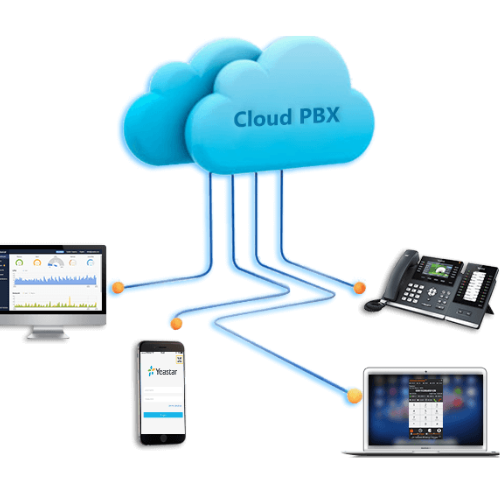
Cloud PBX (Private Branch Exchange): Full Overview
A Cloud PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a cloud-based phone system that allows businesses to manage and route inbound and outbound calls over the internet, eliminating the need for traditional, on-premise PBX equipment. It leverages Voice over IP (VoIP) technology, enabling flexible, scalable, and cost-effective business communications.
Cloud PBX systems are managed by a third-party provider and accessed through the internet, which makes them ideal for businesses looking to reduce infrastructure costs and manage communications with greater flexibility.
1. What is Cloud PBX?
Cloud PBX is essentially a virtual telephone system hosted by a service provider in the cloud. Traditional PBX systems used physical hardware to route internal and external calls within an organization. In contrast, a Cloud PBX provides the same functionality but is hosted remotely, offering many advanced features and integration capabilities.
Instead of connecting phone calls over traditional copper lines or requiring costly hardware, a cloud PBX system routes calls via the internet using VoIP technology.
2. How Cloud PBX Works
With a Cloud PBX system:
- Calls are made or received using IP phones, softphones (applications on computers or mobile devices), or traditional phones with VoIP adapters.
- The call data is transmitted via the internet to the Cloud PBX provider’s servers.
- The provider handles all call routing, switching, and advanced call functions (e.g., voicemail, call forwarding, auto-attendant).
- Incoming calls are directed to the right extensions or teams using automated routing systems (e.g., Interactive Voice Response or IVR).
Because the system operates in the cloud, businesses can manage their phone system via a web-based dashboard, making it easy to add new users, change settings, and monitor call activity.
3. Key Features of Cloud PBX
Cloud PBX systems come with a variety of features that cater to different business needs. Here are the key features:
a) Call Routing and Management
- Automated Call Routing: Routes calls to the correct department or extension based on rules, time of day, or customer input.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): Automated menu systems that allow callers to choose options (e.g., “Press 1 for sales, Press 2 for support”) before being routed to the correct department.
- Call Forwarding: Automatically forwards calls to different numbers or devices based on predefined rules (e.g., after-hours forwarding to mobile phones).
- Ring Groups: Allows multiple phones to ring simultaneously or sequentially to ensure that an incoming call is answered.
b) Voicemail and Voicemail-to-Email
- Offers traditional voicemail, as well as voicemail-to-email functionality, which sends a transcription or audio file of the voicemail to a user’s email.
c) Call Recording
- Allows automatic or on-demand recording of calls, which can be used for training, quality assurance, or compliance purposes.
d) Scalability
- Easily add or remove extensions as needed. Cloud PBX systems can scale up or down based on the number of users without any significant infrastructure changes.
e) Mobile and Remote Access
- Employees can make and receive business calls using their smartphones, laptops, or tablets through mobile or desktop apps, providing remote access to the phone system.
f) Unified Communications (UC) Integration
- Cloud PBX systems often integrate with unified communications platforms, allowing users to manage calls, video conferencing, SMS, and other messaging from a single interface.
g) Conference Calling
- Built-in support for multi-party conferencing, allowing businesses to host conference calls without additional software or hardware.
h) Call Analytics
- Offers detailed reports and real-time analytics on call activity, including call volume, duration, and agent performance.
i) Caller ID & Number Management
- Manage outgoing caller ID, create custom numbers for departments, and utilize DID (Direct Inward Dialing) for specific employees or teams.
4. Benefits of Cloud PBX
The rise of cloud-based systems has led many organizations to adopt Cloud PBX for its flexibility and cost savings. Here are some of the primary benefits:
a) Cost-Effectiveness
- No need for expensive on-premise PBX hardware or maintenance contracts. Cloud PBX operates on a subscription-based model, allowing businesses to pay only for the users or features they need.
- Eliminates costs associated with traditional phone lines, including long-distance or international calling, since all calls are routed via the internet.
b) Scalability
- Cloud PBX systems are highly scalable, allowing businesses to add or remove phone lines, users, or features as their needs grow or shrink. There’s no need for physical hardware changes.
c) Flexibility and Remote Work
- Employees can access the phone system from anywhere, whether they are in the office, working remotely, or traveling. This flexibility is crucial for businesses with distributed or remote teams.
d) Reliability and Redundancy
- Cloud PBX providers generally offer built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms. In case of hardware failures or power outages in one data center, calls can automatically be routed through another.
e) Easy Management
- No need for on-site IT staff to manage or troubleshoot the phone system. All configurations, updates, and system management can be done via an online portal, allowing businesses to quickly make changes.
f) Advanced Features
- Hosted PBX systems come with a wide array of advanced features such as call recording, auto-attendants, advanced call routing, voicemail-to-email, and more — features that are often too costly or complex to implement with on-premise systems.
g) International Access
- For businesses with international clients or offices, Cloud PBX allows seamless global communication, often providing virtual phone numbers in various countries to create a local presence without physical offices.
5. How Cloud PBX is Implemented
Setting up Cloud PBX is usually straightforward:
- Choose a Service Provider: Businesses select a Cloud PBX provider based on their needs, budget, and desired features.
- Set Up the System: The provider will help set up the virtual PBX system, which includes adding users, assigning phone numbers, configuring extensions, and setting up call routing rules.
- Integrate with Devices: Employees can use IP phones, mobile apps, or softphones to connect to the PBX system. These devices will interact with the Cloud PBX over the internet.
- Ongoing Management: Businesses can manage the system via an online portal, where they can add/remove users, monitor performance, and update settings as needed.
6. Use Cases for Cloud PBX
a) Small to Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs)
- SMBs benefit from Cloud PBX because they don’t have to invest in expensive hardware or dedicate IT resources to maintaining the phone system. Cloud PBX scales easily as the business grows, making it ideal for dynamic organizations.
b) Remote and Distributed Teams
- With the growing popularity of remote work, Cloud PBX allows businesses to maintain a unified communications system even when employees are geographically dispersed.
c) Call Centers
- Cloud PBX provides advanced call routing, IVR, and analytics that are crucial for call centers to manage high call volumes and optimize agent performance.
d) International Businesses
- Cloud PBX allows businesses to create a global presence by offering local numbers in different countries, making it easier to communicate with international customers without incurring significant costs.
e) Healthcare
- In healthcare, where secure and reliable communication is critical, Cloud PBX systems can integrate with scheduling systems, enable secure patient communication, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards like HIPAA.
7. Cloud PBX vs. Traditional PBX
| Aspect | Cloud PBX | Traditional (On-Premise) PBX |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Subscription-based, no upfront hardware costs | High upfront cost for hardware and setup |
| Maintenance | Managed by the provider | Requires in-house IT staff or third-party maintenance |
| Scalability | Easily scalable, pay-as-you-go | Limited scalability, often requires new hardware |
| Flexibility | Accessible from anywhere via internet | Tied to physical office location |
| Features | Advanced features, easily upgradable | Limited features, costly upgrades |
| Uptime & Redundancy | High uptime with provider-managed failover | Dependent on in-house infrastructure |
8. Challenges with Cloud PBX
Although Cloud PBX has many benefits, there are a few challenges businesses may face:
a) Internet Dependency
- Since Cloud PBX systems operate over the internet, their performance is highly dependent on a stable and reliable internet connection. In case of internet outages, calls could be disrupted.
b) Call Quality
- Call quality can sometimes be affected by internet bandwidth issues, network congestion, or poor internet connections. Businesses must ensure they have sufficient bandwidth to handle VoIP traffic.
c) Data Security
- With data being transmitted over the internet, businesses must ensure their Cloud PBX provider offers strong encryption and adheres to industry standards for data protection to avoid security breaches.
d) Service Provider Dependency
- The quality, features, and performance of a Cloud PBX system depend on the provider. Businesses should choose a reputable provider with